Arthritis is a common yet debilitating condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It refers to the inflammation and tenderness of one or more joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. In this article, we will delve into the different types of arthritis, their symptoms, available treatments, and effective prevention methods.
Types of Arthritis
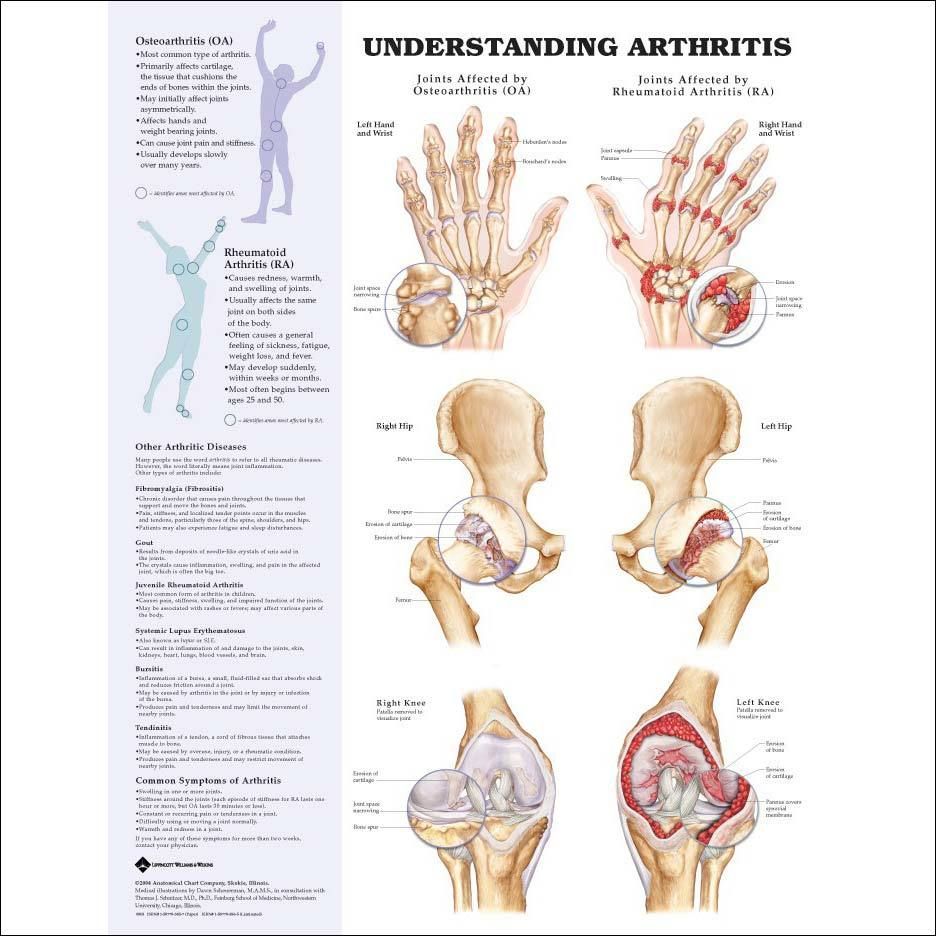
1. Osteoarthritis (OA)
– Described as “wear and tear” arthritis, OA occurs when the protective cartilage on the ends of bones deteriorates over time.
– Common symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced range of motion.
– Age, genetics, obesity, and previous joint injuries are some risk factors for developing OA.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
– RA is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joints, leading to inflammation.
– It commonly affects the hands, wrists, and knees and causes pain, stiffness, fatigue, and joint deformity.
– Women are more prone to developing RA, and it often has a genetic link.
Symptoms of Arthritis
– Joint pain: Persistent discomfort in joints, often worsened with movement.
– Stiffness: Difficulty in moving joints, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
– Swelling: Inflammation and redness around the affected joints.
– Reduced range of motion: Limited ability to move the joints through their full extent.
– Fatigue: Feeling tired and lacking energy, which may result from chronic pain.
– Joint deformity: In advanced cases, arthritis can cause joint deformities and bone spurs.
Available Treatments
1. Medications:
– Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter or prescription medications that alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
– Analgesics: Pain relievers that can be used to manage arthritis symptoms.
– Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs): Prescribed for RA, these drugs slow down the progression of joint damage.
– Biologics: A type of DMARD derived from living organisms to target specific components of the immune system.
2. Physical Therapy:
– Strengthening exercises: Help to build muscle around weakened joints, providing support and reducing pain.
– Range-of-motion exercises: Improve joint flexibility and reduce stiffness.
– Hot and cold therapy: Applying heat or cold packs to affected joints can alleviate pain and inflammation.
3. Surgery:
– Joint replacement: In severe cases, damaged joints, such as hips or knees, can be replaced with artificial joints to improve mobility and reduce pain.
– Synovectomy: Removal of the inflamed synovium (lining of the joint) can reduce pain and prevent further damage.
– Joint fusion: In specific instances, fusing a joint can provide stability and relieve pain.
Prevention Methods
1. Maintain a healthy weight:
– Excess weight puts additional strain on the joints, increasing the risk of developing arthritis.
– Adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity can help manage body weight.
2. Exercise regularly:
– Engage in low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, and walking to strengthen the muscles around the joints.
– Incorporate flexibility exercises to improve joint mobility.
3. Protect your joints:
– Use proper techniques when lifting heavy objects or performing repetitive tasks to avoid joint injuries.
– Use assistive devices, such as braces or splints, when necessary.
4. Stay aware and seek early medical attention:
– Regularly monitor your joint health and consult a healthcare professional if you experience persistent joint pain, stiffness, or swelling.
– Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage arthritis effectively and prevent further damage.
Conclusion
Arthritis affects individuals of all ages and can significantly impact their quality of life. Understanding the symptoms, available treatments, and prevention methods can empower individuals to manage arthritis effectively. By adopting a proactive approach towards joint health, one can alleviate pain, improve mobility, and enhance overall well-being. Consulting with healthcare professionals and staying informed about the latest developments in arthritis research can further aid in the fight against this prevalent condition. Remember, arming yourself with knowledge is an essential step towards overcoming arthritis.