Personalized gene therapy against cancer gets FDA advisory approval
Outside advisors to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration have lent their support to the approval of personalized gene therapy against cancer. The treatment involves reprogramming the patient’s immune system cells and targeting them to destroy cancer cells.
The Food and Drug Agency (Food and Drug Administration, FDA) has been in existence since 1906. Her tasks focus m.in. wok ł food control, drug or medical devices marketed in the US. The agency is known for its rigorous approach, which is why its positive review for a product is considered a kind of quality marker in many countries around the world.
During the panel, experts voted unanimously to support FDA approval of gene therapy. In the release, they said the benefits of the therapy outweigh the risks. – This is a major step forward d, kt ry could usher in a new era – said one advisory, Malcolm Smith, an oncologist at the US National Institutes of Health in Bethesda, Maryland.
If the FDA approves the therapy, it would be the first ever positive review for a therapy using CAR-T technology. It should be noted that the FDA is not obliged to follow the recommendations of its advc, but this is often the case.
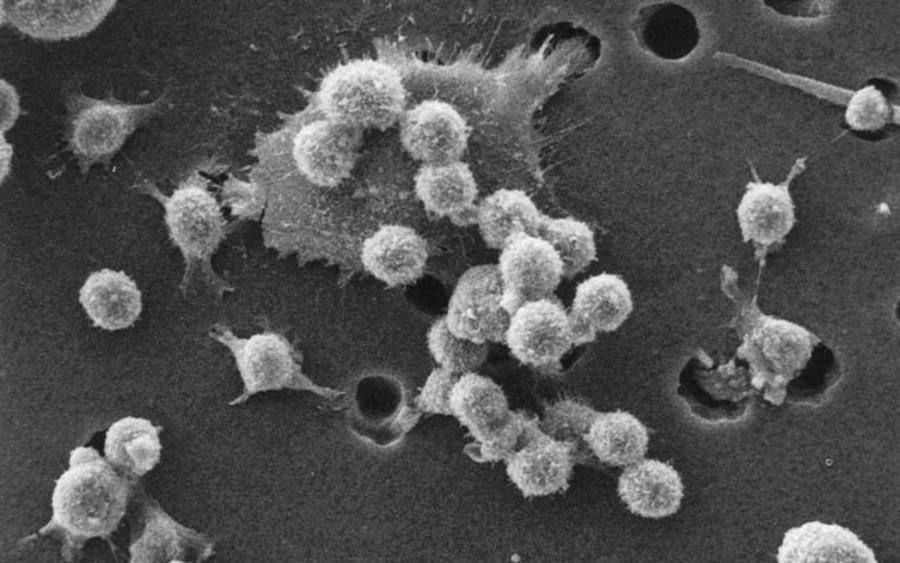
The aforementioned CAR-T immunotherapy involves genetic modification of lymphocytes T – com rec of the immune system – In a particular patient. For these com rek is introduced using a viral vector with an artificial receptor, which ry can recognize the com tumor cells. When such a modified com rka immune system encounters com The cancerous tumor most simply destroys it.
The therapy was developed by the Swiss company Novartis, kt ra wants to treat children suffering from acute lymphoblastic leukemia with its therapy and those who rym patients were not helped by previous anti-cancer therapies.
Tests have shown that CAR-T therapies can cause long-term remissions in such cases. In a key study conducted in 2015, a formulation called tisagenlecleucel developed by Novartis achieved excellent results. In 52 of 63 people b, which re participated in the tests, remission was observed.
However, the therapy carries significant risks. During one study, 47 percent of. participant experienced an extreme inflammatory reaction, potentially life-threatening, called cytokine release syndrome. Successful response of scientists has eliminated the risk in all subjects. In addition to cytokine release syndrome, neurological problems such as seizures and hallucinations were common symptoms, but they occurred temporarily.
In other studies conducted last year on the CAR-T technique, there were even reported cases of death due to severe edema m zgu. But Novartis’ therapy is different from those used in feral pr bach. However, these have swayed the perception of the entire method.
Tisagenlecleucel is prepared for each patient separately. First, the cells are taken rki of a patient who re then subjected to genetic engineering. Thus prepared rks are cultured before they are given to the patient. It takes about 22 days to prepare a drug for a particular patient.
CAR-T therapy is high-risk and little is known about the long-term effects of the in its use. However, patients to whom the rym targeted by the therapy, they do not have many alternatives.
Pictured is the process of com death cancer rec .
Source Source: Nature, The Washington Post, fot. National Cancer Institute/Wikimedia Commons