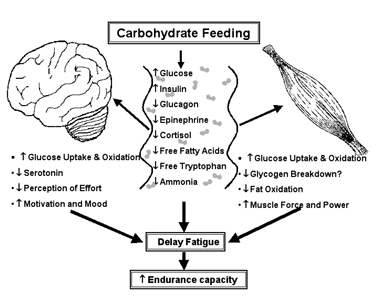
Endurance sports, such as long-distance running, cycling, and swimming, require athletes to sustain high levels of physical exertion for extended periods. To achieve optimal performance, athletes need to fuel their bodies with the right nutrients, with carbohydrates playing a crucial role in providing the energy necessary for the demands of endurance sports.
The Importance of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for our bodies. When consumed, they are broken down into glucose, which is then used as fuel for our muscles and brain. In endurance sports, a significant amount of energy is expended, making it vital for athletes to consume adequate amounts of carbohydrates to replenish their glycogen stores and maintain performance.
Glycogen Depletion and Fatigue
Engaging in endurance activities depletes the glycogen stores in the muscles and liver. Glycogen is the stored form of glucose, and when it runs out, athletes experience fatigue and a decrease in performance. By consuming carbohydrates before, during, and after exercise, athletes can help prevent glycogen depletion and delay the onset of fatigue.
Pre-Exercise Carbohydrate Loading
Carbohydrate loading is a strategy often employed by endurance athletes to maximize glycogen stores before a long and intense event. It involves consuming a high-carbohydrate diet and tapering exercise in the days leading up to the event. This method has been shown to increase glycogen stores, improving endurance and performance.
Carbohydrate Intake during Exercise
During prolonged exercise, it is crucial to provide a steady supply of carbohydrates to maintain energy levels and delay fatigue. Consuming easily digestible carbohydrates in the form of gels, sports drinks, or energy bars can help sustain glycogen stores and prevent hypoglycemia. The recommended intake varies depending on the duration and intensity of the activity, but typically ranges from 30-60 grams of carbohydrates per hour.
Post-Exercise Carbohydrate Consumption
Immediately after exercise, the body is more efficient at replenishing glycogen stores. Consuming carbohydrates within the first 30-60 minutes after exercise can enhance glycogen synthesis and reduce the time required for recovery. Including both simple and complex carbohydrates in the post-workout meal or snack is essential for optimal recovery.
The Glycemic Index and Endurance Sports
The glycemic index (GI) is a scale that ranks carbohydrates based on how quickly they raise blood glucose levels. In endurance sports, it is beneficial to consume carbohydrates with a moderate to high GI before and during exercise. These carbohydrates are quickly digested and provide a rapid release of glucose, supplying the body with immediate energy.
The Importance of Timing and Individualization
While carbohydrates are fundamental for endurance sports, there is no one-size-fits-all approach to carbohydrate intake. Each athlete has unique energy demands, and it is crucial to experiment and find the timing, amount, and types of carbohydrates that work best for individual needs. Some athletes may find that they perform better with more complex carbohydrates or a combination of different sources, while others may benefit from a higher intake of simpler carbohydrates.
Conclusion
Carbohydrates play a vital role in powering endurance sports. By consuming the right types and amounts of carbohydrates, athletes can sustain their energy levels, delay fatigue, and optimize performance. Recognizing the significance of carbohydrate intake, both before, during, and after exercise, and tailoring it to individual needs, endurance athletes can reach their full potential and achieve their goals.

